India Macro Pulse March 2025
Gain exclusive insights into GDP trends, inflation dynamics, industrial performance, banking liquidity, trade developments, energy consumption, and the booming automotive sector.
Unlock India's Economic Momentum. The key highlights:
Q3 GDP performance and revised FY forecasts
Headline CPI below 4% and rising core inflation trends
Industrial production and sectoral performance
Banking liquidity, credit & deposit trends
Trade imbalances and external sector risks
Fuel consumption and automotive sector performance
1. Growth & GDP Outlook
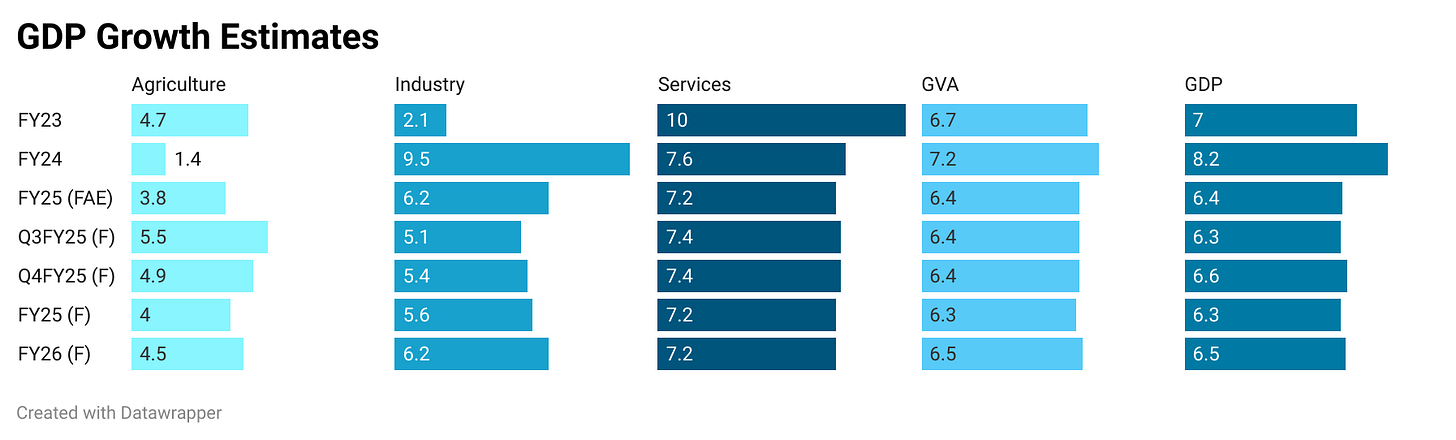
Q3FY25 GDP Highlights:
Growth Rate: Q3FY25 GDP came in at 6.2% YoY, slightly below earlier expectations of 6.3%.
Revised Projections: FY25 growth estimates have been revised upward to around 6.5% (from 6.4%), reflecting improved consumption demand—particularly rural—and higher government capital spending.
Key Drivers:
Rural Consumption: Buoyant agricultural output and government support programs have helped sustain higher rural incomes, boosting spending on FMCG, tractors, and two-wheelers.
Government Capex: A 48% jump in Q3 central government capex (per references) has provided a fillip to infrastructure, roads, and railways, indirectly stimulating sectors like cement, steel, and commercial vehicles.
Private Consumption & Services: Renewed urban demand—albeit weaker than rural—has started picking up, supported by a recent tax cut, healthy services exports, and robust travel/tourism.
Looking Ahead:
The FY25 GDP forecast is ~6.5% YoY, with further improvement likely in FY26 (6.5–6.6% range) if global conditions remain stable and private capex begins to accelerate.
2. Inflation & Prices
Headline and Core CPI
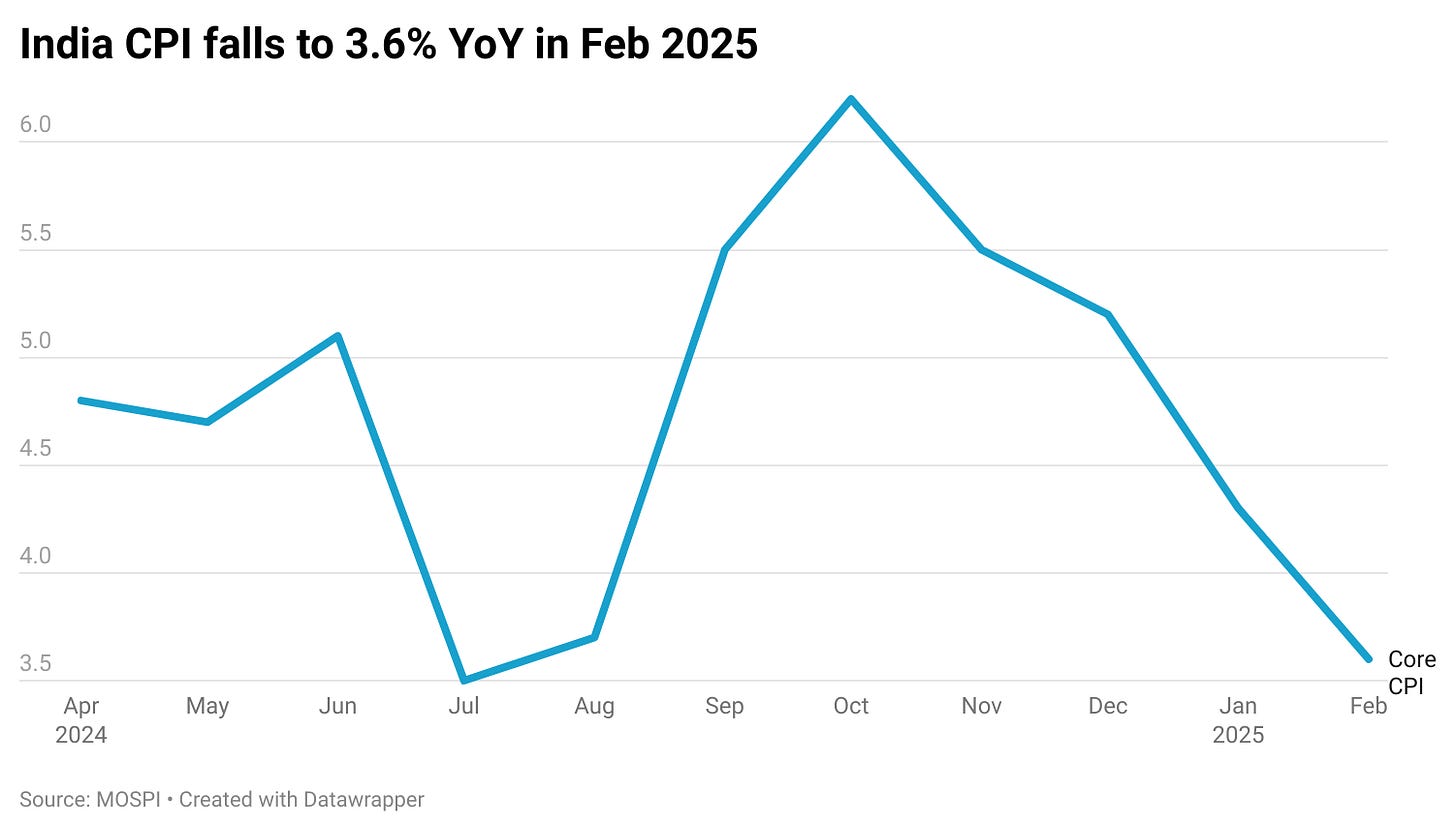
Headline CPI:
Eased to ~3.6% YoY in February 2025, significantly lower than the 4.26% YoY recorded in January.
The main contributor is a steep drop in food inflation (down to around 3.7% YoY).
Core CPI:
Edged up slightly to ~4.0% YoY, driven by categories like personal care & effects (precious metals) and certain service segments.
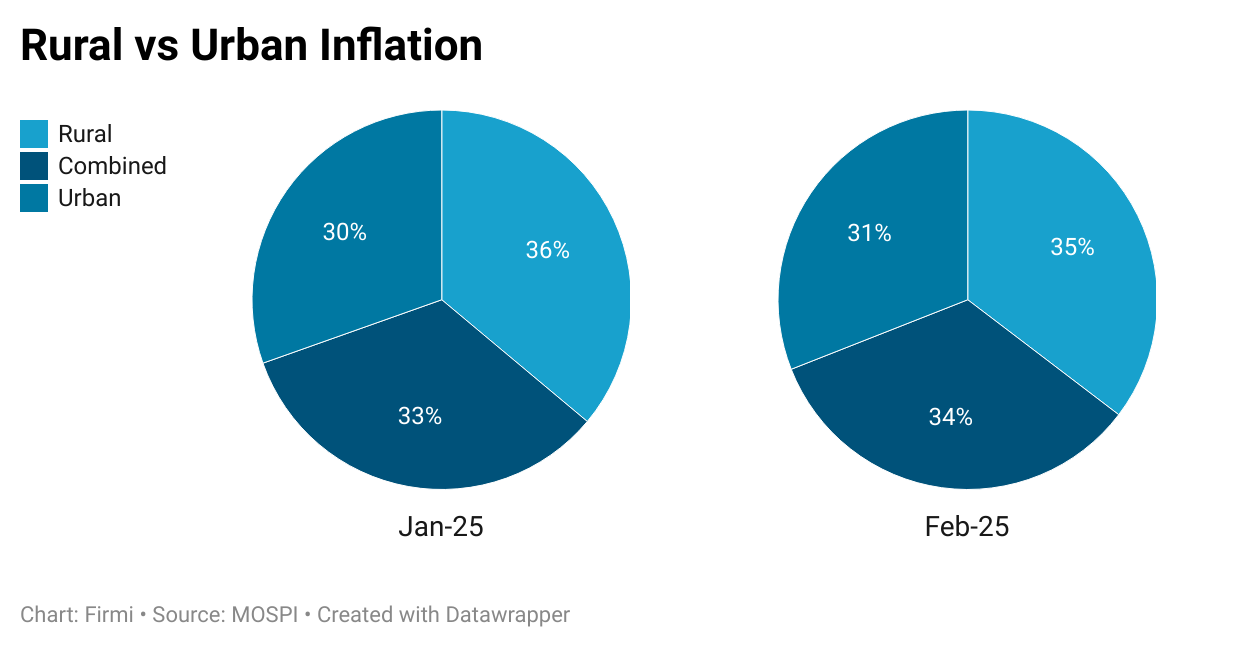
Food vs. Non-Food Dynamics
Food Basket:
Vegetables, pulses, and eggs registered notable MoM price declines, reflecting improved supply chains and stable commodity costs.
A normal monsoon forecast and stable fertilizer prices could keep food inflation contained in coming months.
Fuel & Energy:
Global oil prices have been relatively subdued, helping moderate transportation and logistics costs.
Policy Implications
RBI Leeway: With headline CPI well under 4%, the Reserve Bank of India may consider maintaining or slightly easing policy rates if growth signals soften.
Watchpoints: Potential upside risks if global commodity prices rebound or if monsoon outcomes deviate from forecasts.
3. Industrial Production & Sectoral Performance
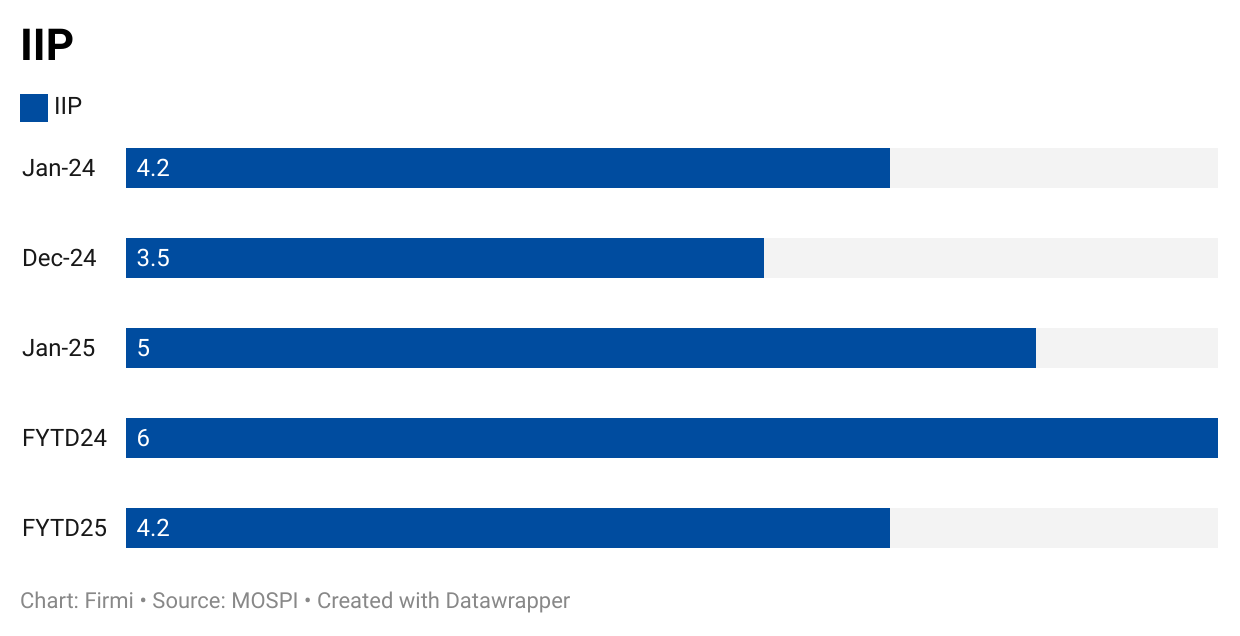
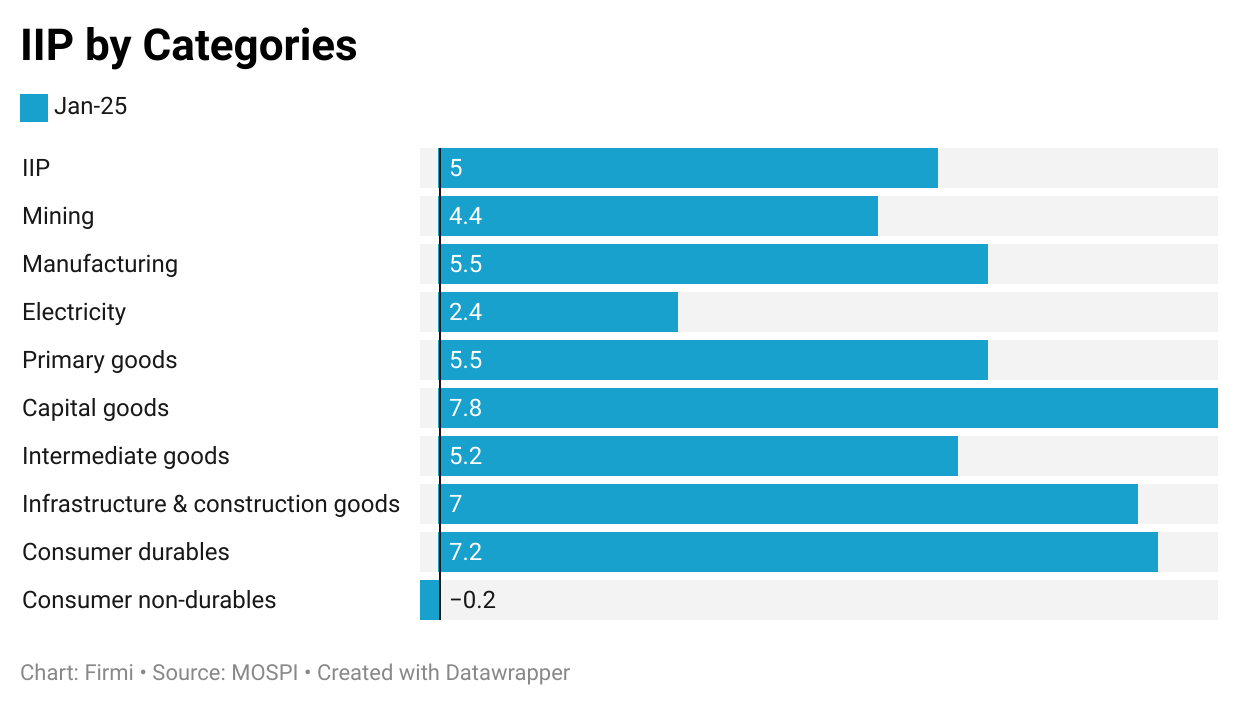
IIP Growth
Overall IIP: Rose to 5.0% YoY in January 2025 (from 3.5% in December 2024).
Manufacturing: +5.5% YoY, underpinned by capital goods (+7.8% YoY), infrastructure & construction goods (+7.0%), and consumer durables.|
Sector Insights
Capital Goods: Bolstered by government infrastructure projects and private sector investments in machinery and equipment.
Infrastructure & Construction: Cement production has grown steadily; steel consumption also remains robust despite short-term monthly fluctuations.
Electricity & Mining: Showed moderate improvements; however, electricity generation has been mixed, partly reflecting weather patterns and industrial usage.
4. Banking & Financial Indicators
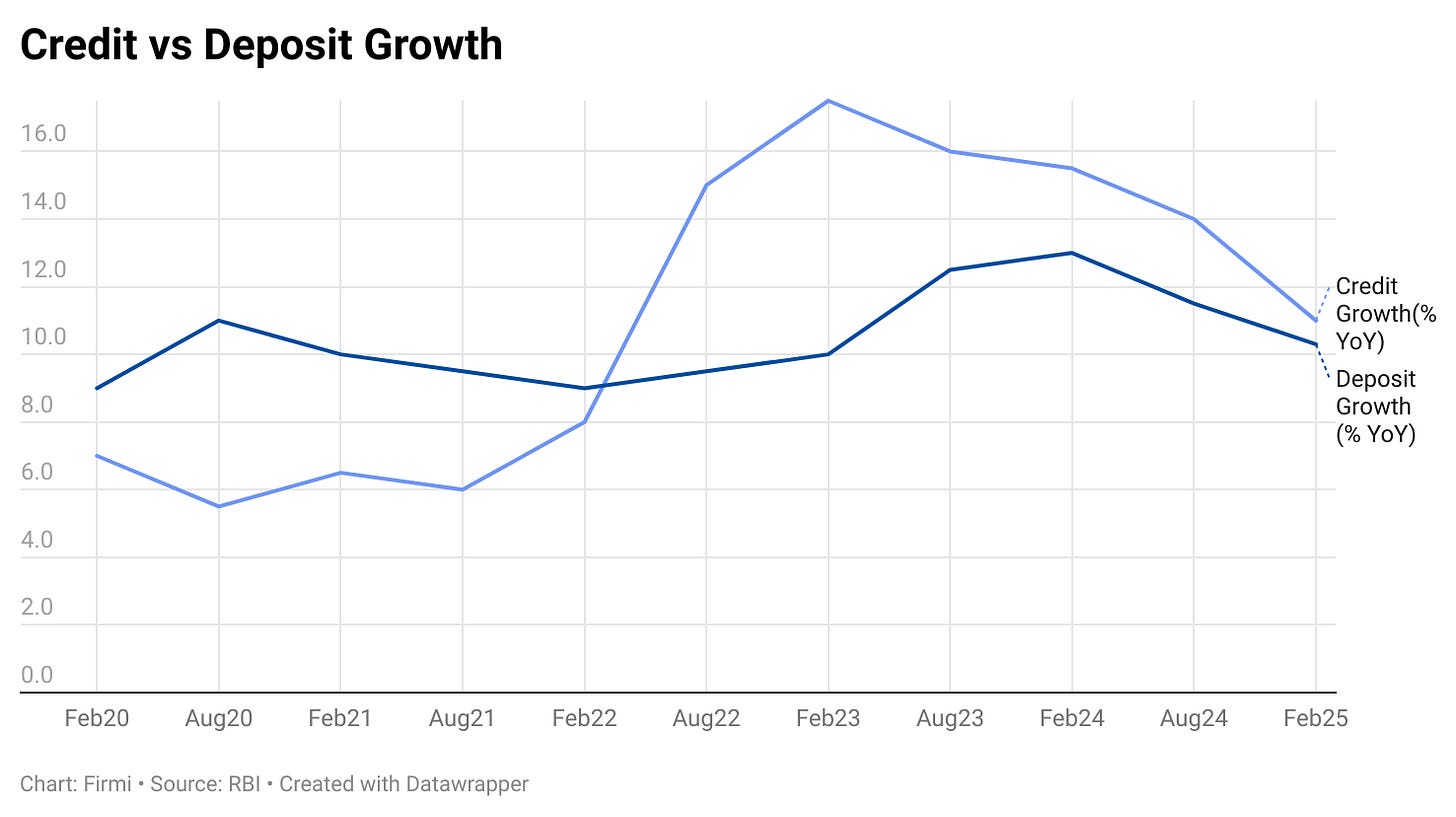
Credit and Deposits
Credit Growth: Decelerated from above 15% YoY in mid-2024 to ~11% YoY by February 2025.
Deposit Growth: Slowed from ~12% YoY to 8% YoY over the same period, signaling potential liquidity pressures for banks if the trend persists.
Liquidity and Interest Rates
RBI Interventions: The central bank has injected liquidity via INR 1tn of OMO purchases and a USD 10bn FX swap, which has helped stabilize yields.
SDL Spreads: High state government borrowings have widened SDL–G-sec spreads to ~13-month highs.
Outlook
Banking Strategy: Banks may raise deposit rates or introduce new products to attract savers. Targeted lending in resilient sectors (infrastructure, retail, renewables) could support balanced credit growth.
5. External Sector & Trade
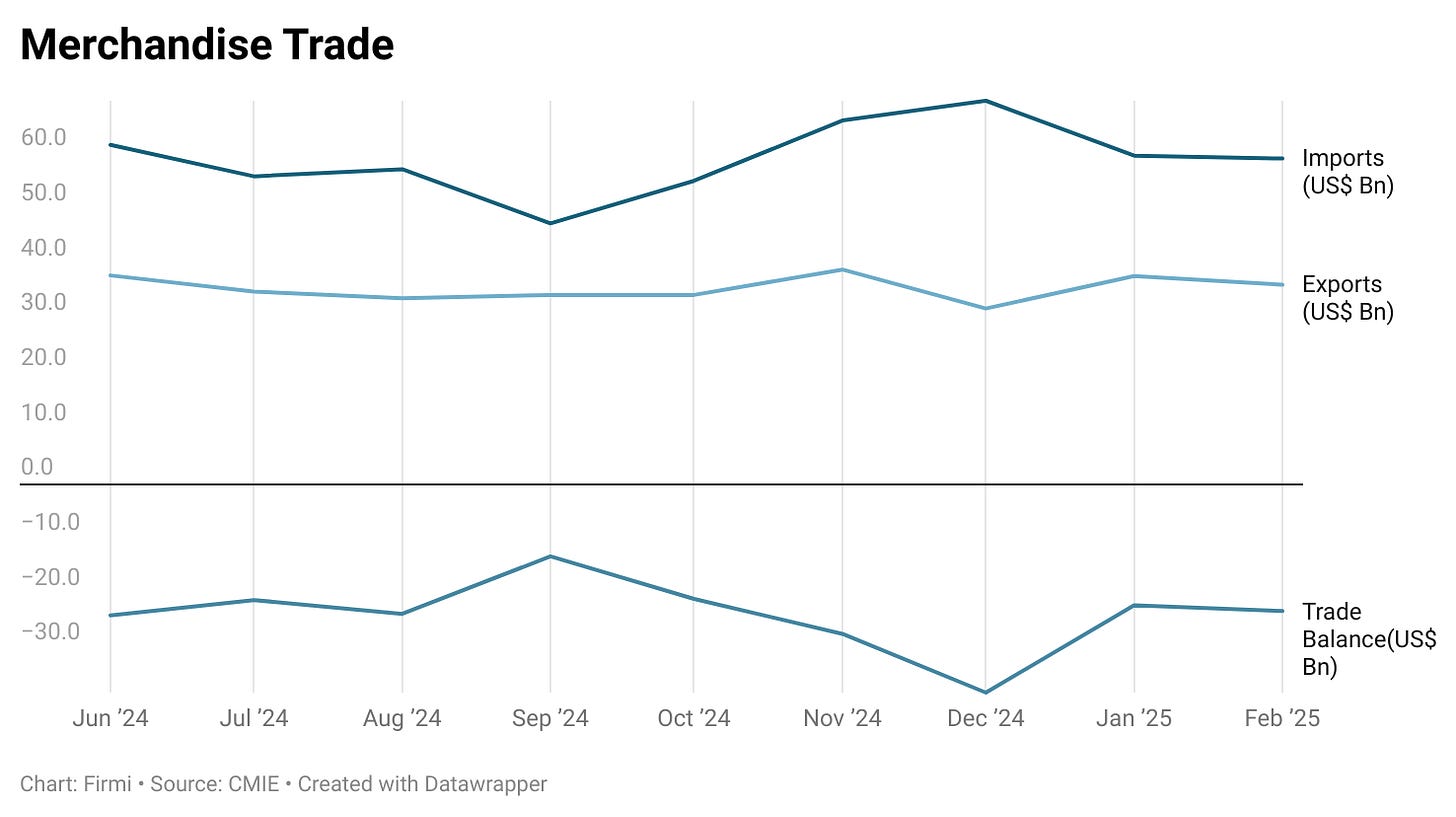
Merchandise Trade
Deficit Trend: Merchandise trade deficit has widened in recent months, partly driven by a surge in gold imports and energy prices.
Exports: Some deceleration amid weaker global demand, though certain categories (e.g., electronics, pharma) remain stable.
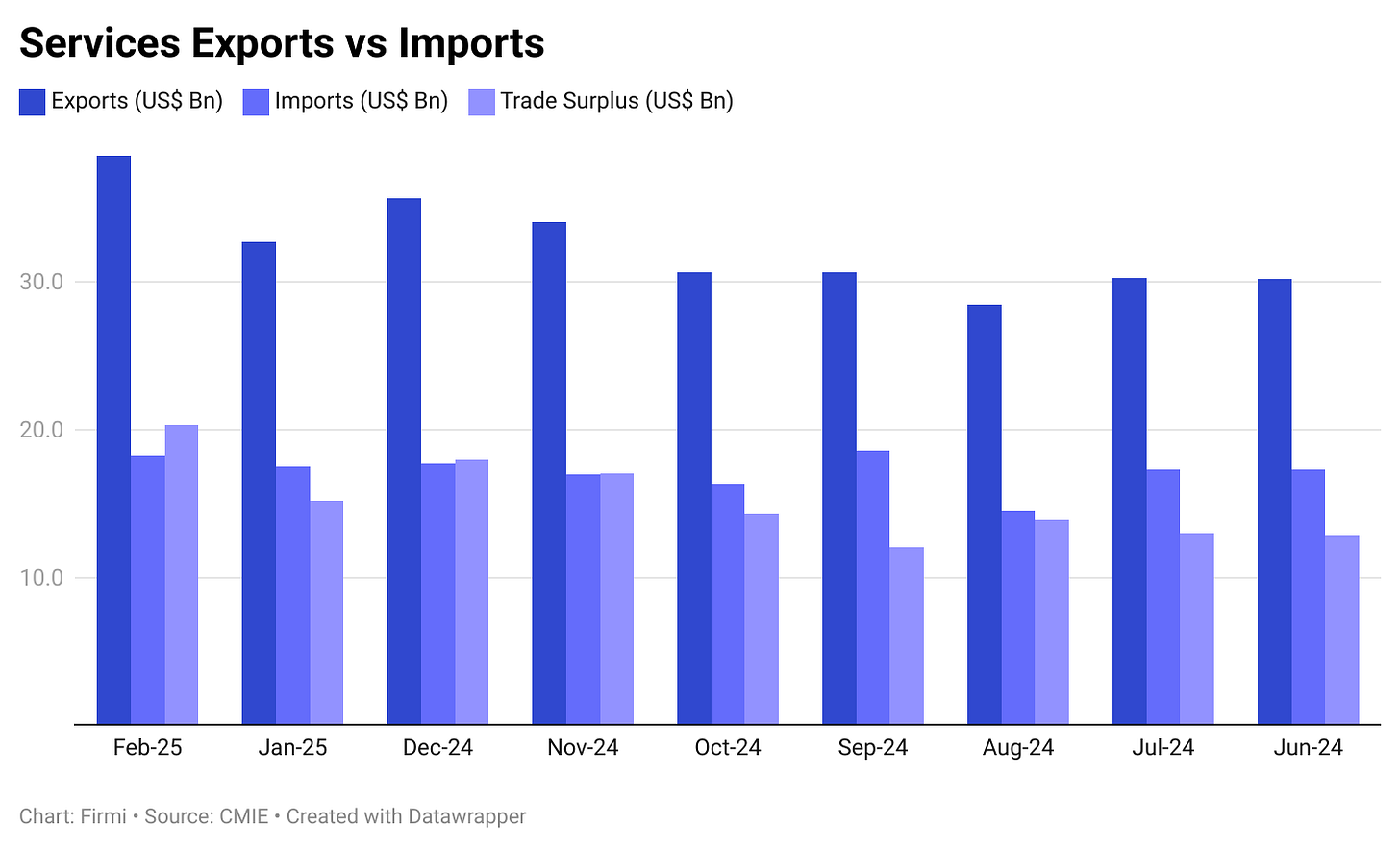
Services Trade
IT & Services Surplus: Continues to expand, helping offset merchandise deficits. Services exports have grown ~17% YoY, per the India Economic Monitor.
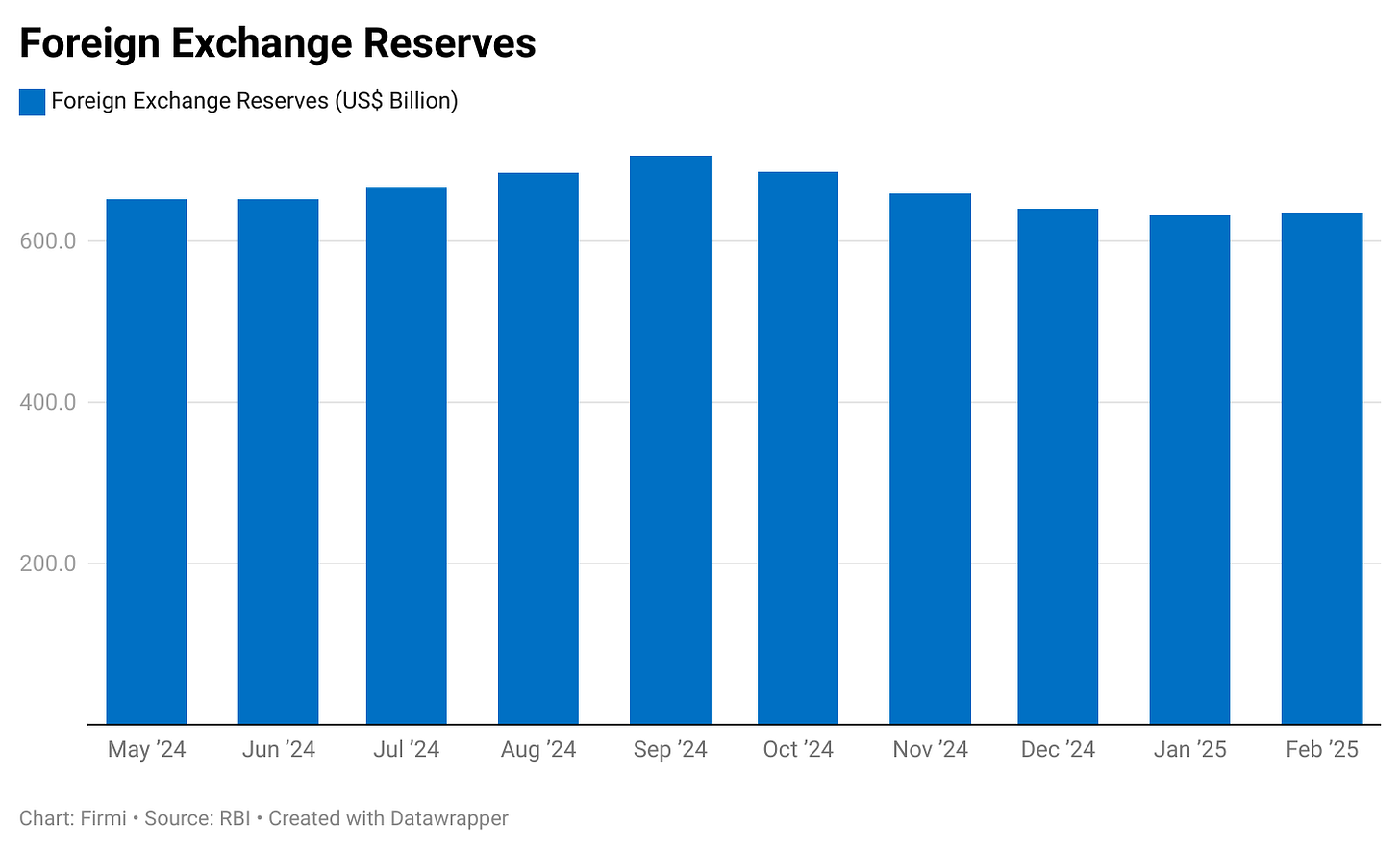
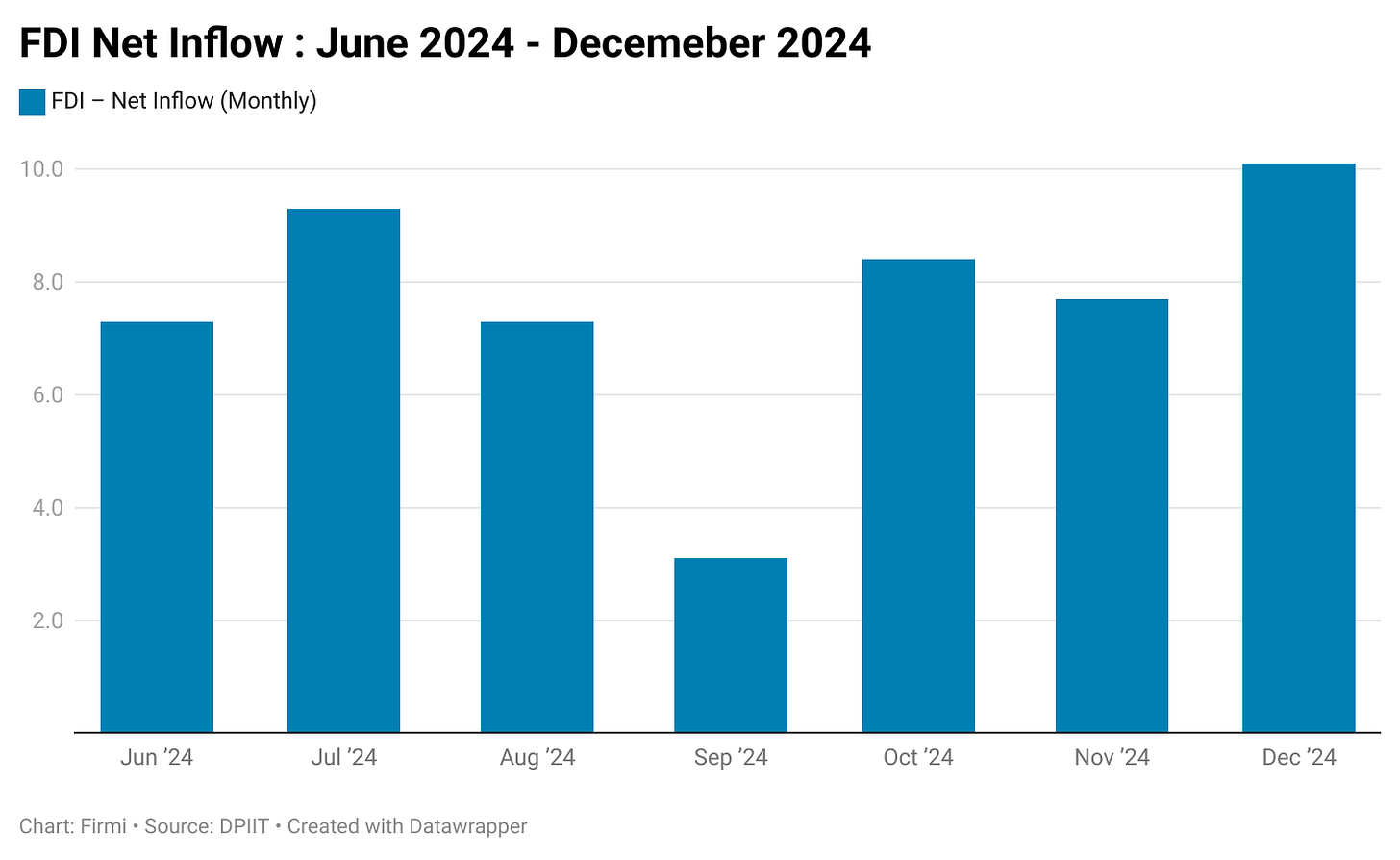
Forex & FDI
Forex Reserves: Under pressure due to RBI interventions (to stabilize INR) and FPI outflows.
FDI Flows: Notable volatility; a rebound in December 2024 was followed by a decline in early 2025. Overall, 2024 FDI was lower than 2023 levels, reflecting global uncertainty.
6. Fuel Consumption & Energy Indicators
Fuel Consumption Drop
Seasonally Adjusted MoM Change (Feb–Mar 2025): The new chart shows a steep drop in monthly fuel consumption growth, possibly reflecting:
Post-Festive Slowdown in industrial and transportation demand.
Increased EV Adoption in two- and three-wheeler segments.
Global Oil Prices: Softer crude prices reduce costs, but volatility can still disrupt consumption patterns.
Electricity & Renewables
Electricity Generation: Moderate upticks tied to industrial activity.
Renewable Energy: Continues to expand capacity, though generation volumes fluctuate seasonally.
7. Automotive Sector: Detailed Segment Analysis
Passenger Vehicles (PVs)
OEM Dispatches vs. Registrations:
OEMs report sustained YoY sales growth, reflecting optimism and restocking at dealerships.
Registrations (LMVs) show occasional dips, suggesting a wholesale-retail mismatch or inventory buildup.
Outlook: With stable inflation and improving consumer sentiment, the PV segment is poised for continued growth, especially in mid-range and premium categories.
Two-Wheelers (2W)
Sales Trends:
Recovering post-festive lull; rural demand remains a critical driver.
EV 2W penetration is slowly climbing, impacting petrol consumption.
Three-Wheelers (3W)
Urban Mobility & Last-Mile:
Growth supported by e-commerce, last-mile connectivity, and ride-sharing.
Electric 3W options are gaining traction in select urban markets.
Commercial Vehicles (CVs)
Mixed Growth:
Medium-to-heavy CVs benefit from government infrastructure projects.
Light CVs see steady demand from e-commerce expansions, though freight rate fluctuations keep operators cautious.
Tractors
Rural Strength:
Healthy rabi crop output and government procurement programs support sales, though momentum slowed slightly post-festive.
Tractor demand remains closely tied to monsoon outcomes and rural credit availability.
8. Key Fiscal & Consumption Indicators
GST Collections
GST Revenues: Averaged ~INR 1.8–1.9 trillion/month, up ~9–10% YoY (as per monthly data from India Economic Monitor).
Implication: Stable collections point to ongoing formalization and consumption resilience, especially in the services and manufacturing sectors.
Consumer Confidence & Spending
PMI Readings: Manufacturing PMI ~56–57 range; Services PMI near 58–59 in recent prints, reflecting expansion.
Household Consumption: Lower inflation and targeted government support (e.g., rural subsidies, tax cuts) help maintain spending levels, especially in FMCG and lower-priced consumer durables.
9. Outlook & Recommendations
Macro Outlook
Growth Trajectory: FY25 GDP likely at 6.5% YoY, underpinned by government spending, robust rural demand, and moderate inflation.
Inflation Risks: While food inflation is subdued, any commodity price rebound or erratic monsoon could reignite price pressures.
Monetary Policy: With headline inflation below 4%, the RBI may maintain an accommodative stance or enact a mild rate cut if growth signals soften further.
Strategic Implications
Banking & Liquidity Management:
Banks should focus on deposit mobilization strategies and prudent lending to sectors showing resilient demand (infrastructure, housing, green energy).
Automotive Sector:
OEMs must calibrate production to avoid overstocking as the gap between dispatches and registrations persists.
EV investment remains key, especially in 2W and 3W categories, given the emerging shift in fuel consumption patterns.
Investors & Corporates:
Focus on domestic consumption plays (FMCG, autos, retail lending).
Watch global commodity movements and trade policy changes that could impact exports and input costs.
Risk Factors
Global Headwinds: Potential slowdowns in the US, EU, or China can affect India’s exports and FDI inflows.
Commodity & Oil Price Volatility: A sudden spike could squeeze margins and reverse inflation gains.
Monsoon Variability: A subpar monsoon would dampen rural incomes and raise food inflation.
10. Concluding Remarks
India’s macroeconomic fundamentals appear solid, with 6.2% GDP growth in Q3 and inflation below 4%. While bank credit and deposit growth have decelerated, the RBI’s liquidity measures and robust government capex provide buffers against potential headwinds. The auto sector—a bellwether for consumer confidence—remains largely optimistic, even as fuel consumption data signals changing mobility patterns and potential shifts toward EVs.
Overall, maintaining stable inflation, sustaining consumption, and fostering a supportive credit environment will be vital for India to uphold its ~6.5% growth trajectory in FY25 and beyond.